全球首次:时序大模型突破十亿参数,华人团队 Time-MoE 预训练数据达 3000 亿个时间点
Time-MoE utilizes an innovative mixture of experts architecture, achieving high-precision predictions at a lower computational cost. The research team has also released the Time-300B dataset, which provides extensive training resources for time series analysis, offering new solutions for forecasting tasks across various industries.

In today\’s data-driven era, time series forecasting has become a vital core component across many domains. However, building a large-scale time series forecasting model that combines strong performance with efficient computation has always been a significant challenge. Additionally, the lack of high-quality large public time series databases has exacerbated this issue.
Recently, an international research team comprising Chinese scholars from Princeton University, Griffith University, and other institutions has collaborated to innovatively propose Time-MoE, a foundational model for time series based on the mixture of experts (MoE) architecture. This development marks a milestone by pushing the parameter scale of pre-training time series large models into the billion range, achieving groundbreaking advancements in time series forecasting.

Simultaneously, the team meticulously curated the pre-training dataset Time-300B, currently the largest publicly available dataset in the field of time series, which offers unprecedented general solutions for various time series tasks. This marks the first instance of utilizing such a large-scale pre-training model in the time series domain, heralding the onset of a new era in time series forecasting technology.
The Time-MoE model, leveraging the unique advantages of the MoE architecture, successfully expands the model parameters to 2.4 billion, significantly enhancing prediction accuracy while reducing computational costs, thus surpassing many existing models and achieving State of the Art (SOTA) performance across the board.
关键技术突破
1. 强大的混合专家架构:Time-MoE 采用稀疏激活机制,在预测任务中仅激活部分网络节点,这不仅确保了高预测精度,还显著降低了计算负担,完美解决了时序大模型在推理阶段的计算瓶颈。
2. 灵活的预测范围:Time-MoE 支持任意长度的输入和输出范围,能够处理从短期到长期的各种时序预测任务,实现了真正的全域时序预测。
3. 全球最大规模的开源时序数据集:团队开发了 Time-300B 数据集,涵盖 9 个领域的超过 3000 亿个时间点,为模型提供了丰富的多领域训练数据,确保其在多种任务中的卓越泛化能力。
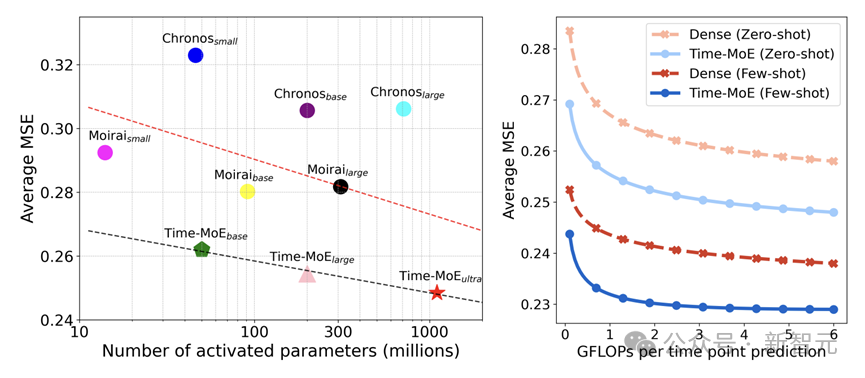
在相同激活参数条件下,Time-MoE 显著超越了现有的时序基础模型。在相同的 FLOPs 下,其稀疏架构展现出相较于密集模型的卓越精度优势。
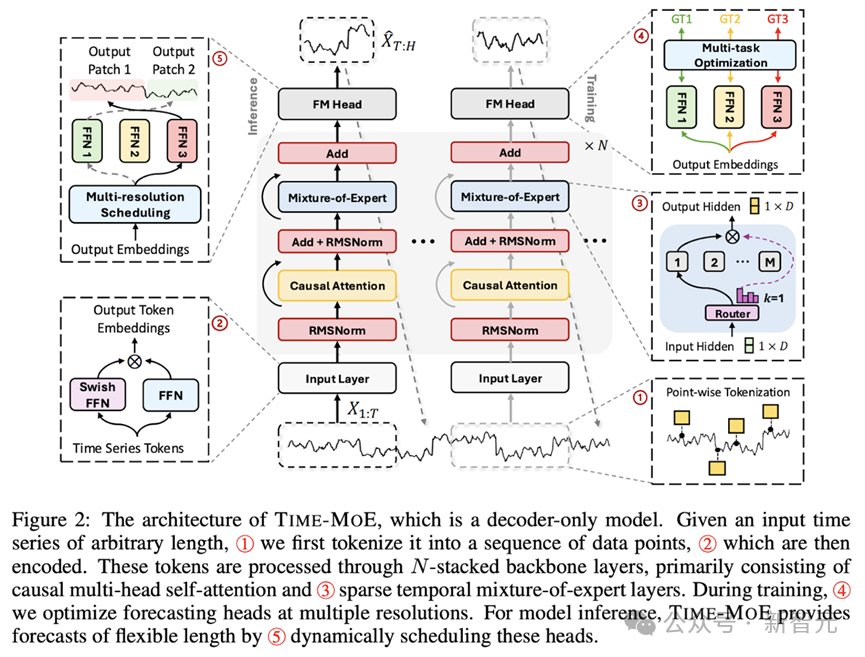
模型框架
输入 Token Embedding
Time-MoE 使用逐点分词方法以确保时间序列信息的完整性,提高了模型处理不同长度序列的灵活性与适用性,如模型框架图中①所示。在②中,SwiGLU 激活函数对每个时间序列点进行嵌入,其中包括一个 Feed-forward network (FFN) 和一个 Swish FFN,从而增强模型对多维输入的处理能力:
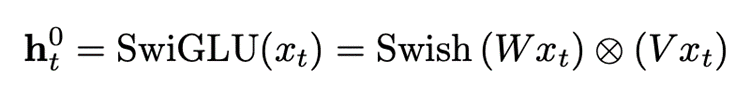
MoE Transformer 模块
Time-MoE 基于 decoder-only Transformer,并结合了大规模语言模型中的最新技术。Transformer 模块里,RMSNorm 对每个子层输入进行了归一化处理,从而提升了训练的稳定性。
同时,采用旋转位置编码代替绝对位置编码,使得模型在处理可变序列长度时具备更好的外推能力。此外,模型引入了稀疏激活的混合专家层来取代标准 Transformer 模块里的 FFN。
公式化概括如下:
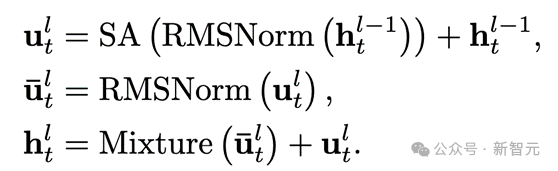
其中 Mixture 代表混合专家层。如模型框架图中③所示,单个时间序列数据点可以被分配给一个或多个专家。通过选择部分专家网络来处理特定时间点的输入,模型的计算效率得到了提高。
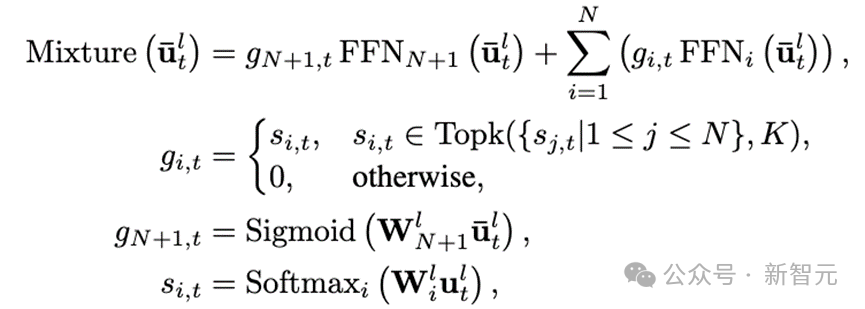
多分辨率预测
如模型框架图中④和⑤所示,Time-MoE 设计了一种多分辨率预测头,可以同时进行不同尺度的预测,突破了单一尺度预测的局限。
在训练时,不同分辨率头会被联合优化。在与推理时,模型采用贪心算法,利用不同尺度的输出组合成任意的预测长度。这种设计允许模型根据不同的预测范围进行灵活预测,并在训练过程中综合多个预测尺度的误差来优化模型的泛化能力,从而显著提升预测的准确性和鲁棒性。
实验效果
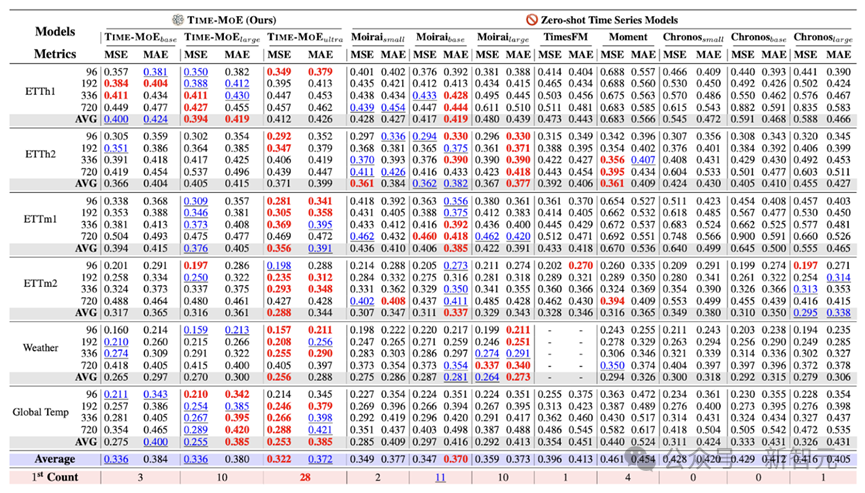
1. 零样本 zero-shot 预测
零样本预测能有效检验时序基础模型的泛化能力和通用性。实验表明,与现有的时序基础模型相比,Time-MoE 达到了最好的预测效果,均方误差(MSE)降低了约 20%。
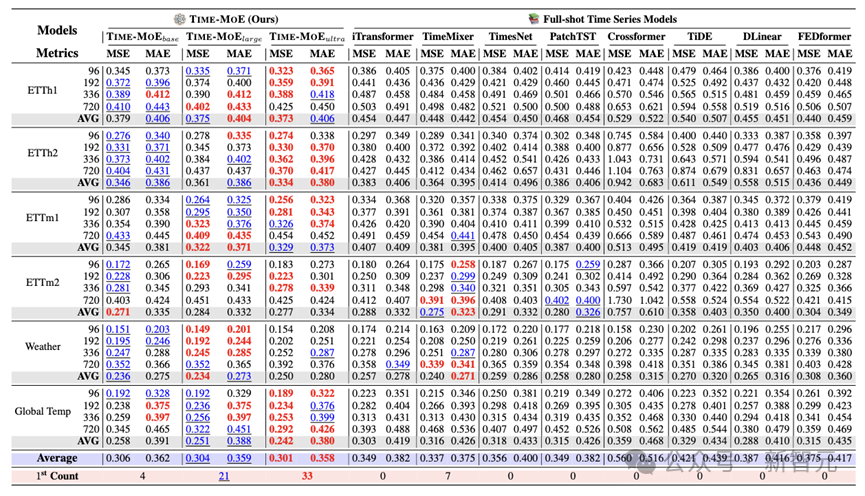
2. 全样本 full-shot 预测
在全样本预测中,预训练的 Time-MoE 会使用相应数据的训练集进行微调。实验表明,与专门为全样本预测设计的时序模型相比,Time-MoE 依然能达到最优的效果,MSE 降低了约 24%。这体现了模型对于不同领域数据的适用性,以及预训练基础模型对于下游任务帮助的有效性。
3. 消融实验
文中进一步提供了一系列消融实验来验证模型框架设计的合理性。实验表明,Time-MoE 的设计在提升模型精度上是有效的。特别地,在不使用混合专家的情况下,模型的 MSE 会有明显的退化。

4. Scalability 分析
作者对于模型的规模化效果进行了详细分析,如下图所示。左图的实验表明,与稠密模型相比,稀疏模型减少了平均 78% 的训练成本和 39% 的推理成本。
右图的结果表明,随着数据量和模型参数的增大,Time-MoE 持续表现出稳定的性能提升,并且与同规模的稠密模型相比,总能达到更小的 MSE 和更好的预测性能。
此外,作者还分析了训练精度的影响。如下表所示,与使用 float32 精度进行训练相比,使用 bfloat16 精度能得到相似的预测性能,但是 bfloat16 模型能在训练速度上获得 12% 的提升,内存占用上有 20% 的减少。
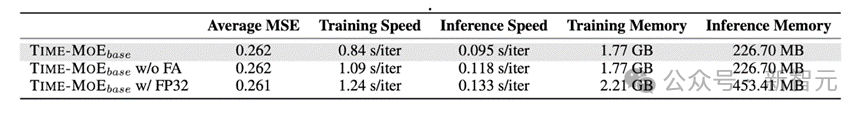
此外,bfloat16 还可以与 flash-attention(表中简称为 FA)无缝结合,从而进一步在训练和推理速度上带来 23% 和 19% 的提升。
总结
Time-MoE 的成功标志着时序预测领域迈入了一个全新时代。它不仅在性能上全面超越了现有模型,更为构建大规模、高效、通用的时序预测基础模型奠定了一个可行的范式。Time-MoE 的发布不仅为学术界开辟了全新的研究方向,也为工业界的多种时序应用场景注入了巨大的潜力。在能源管理、金融预测、电商销量、气象预报等众多关键领域,Time-MoE 将成为企业和研究机构的强大工具。
团队成员相关论文:
-
[1] Foundation Models for Time Series Analysis: A Tutorial and Survey, KDD 2024.
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.14735
-
[2] Large Models for Time Series and Spatio-Temporal Data: A Survey and Outlook, arXiv 2023
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.10196
-
[3] Position: What Can Large Language Models Tell Us about Time Series Analysis, ICML 2024.
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.02713
-
[4] Time-LLM: Time Series Forecasting by Reprogramming Large Language Models, ICLR 2024.
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.01728
-
[5] TimeMixer: Decomposable Multiscale Mixing for Time Series Forecasting, ICLR 2024.
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.14616
-
[6] iTransformer: Inverted Transformers Are Effective for Time Series Forecasting, ICLR 2024.
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.06625
-
[7] TimeMixer++: A General Time Series Pattern Machine for Universal Predictive Analysis, arXiv 2024
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2410.16032
-
[8] Towards Neural Scaling Laws for Time Series Foundation Models, arXiv 2024 https://www.arxiv.org/pdf/2410.12360
-
[9] Time-MMD: A New Multi-Domain Multimodal Dataset for Time Series Analysis, NeurIPS 2024.
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.08627
-
[10] Time-FFM: Towards LM-Empowered Federated Foundation Model for Time Series Forecasting, NeurIPS 2024.
-
https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.14252